Abstract
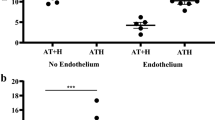
PHENOLS counteract the antithrombic activity of plasma and serum1. The antithrombic activity is present in a protein fraction which also contains the co-factor required for the anticoagulant effect of heparin2. The antithrombic and the heparin co-factor activity are present in the α-globulin fraction of human plasma3. It was therefore of interest to test the influence of phenols on heparin activity in plasma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fantl, P., Biochem. J., 57, 416 (1954).
Howell, W. H., and Holt, E., Amer. J. Physiol., 47, 328 (1918).
Lyttleton, J. W., Biochem. J., 58, 15 (1954).
Gerber, C. F., and Blanchard, E. W., Amer. J. Physiol., 44, 447 (1945).
Homan, T. D. H., and Lens, F., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2, 333 (1948). Monkhouse, F. C., and Jaques, L. B., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 36, 782 (1950).
Weissbecker, L., and Hitzelbieger, A., Klin. Wochenschr., 31, 288 (1953). Köhler, V., Naturwiss., 42, 99 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FANTL, P., MARR, A. Phenols as Inhibitors of the Heparin Co-factor of Plasma. Nature 180, 990 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1038/180990a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/180990a0