Abstract
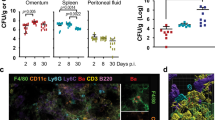
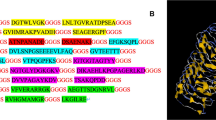
THE distribution of radioactively labelled antigens in animal tissues has been studied extensively. Most of the work has been done in normal animals, using simple antigens. Few direct comparisons have been made of the distribution of labelled antigens in normal and immune animals, and no work seems to have been done along these lines with a killed bacterial antigen.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFarlane, A. S., Biochem. J., 62, 135 (1956).
Sulitzeanu, D., Refuah Veterinarith., 13, 111 (1956).
Ingraham, J. S., J. Inf. Dis., 89, 117 (1951).
Fitch, F. W., Barker, P., Soules, K. H., and Wissler, R. H., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 42, 598 (1953).
La Via, M. F., Barker, P. A., and Wissler, R. W., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 48, 237 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SULITZEANU, D. Distribution of Radioiodinated, Acetone-killed Brucella abortus in the Tissues of Normal and Immune Mice. Nature 181, 495 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/181495a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/181495a0