Abstract
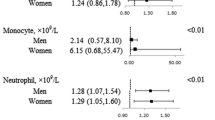
DURING an investigation of the respiration of human leucocytes we noticed that moderate exercise by the donor prior to venepuncture seemed to be associated with a high rate of leucocyte oxygen consumption. Determination of the oxygen consumption of leucocytes (resuspended in a modified Krebs No. 2 buffer) was-made by the direct method in Warburg respirometers at 37° C. Results were expressed as μmoles oxygen consumed per hr. per 107 leucocytes, so that the effect of any variation in total white cell count was eliminated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BISSET, S., ALEXANDER, W. Effect of Muscular Activity prior to Venepuncture on the Respiration of Leucocytes in vitro . Nature 181, 909–910 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/181909b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/181909b0