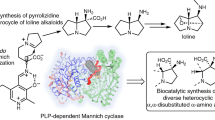
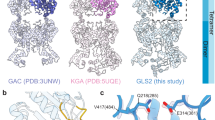
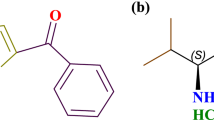
Abstract
GLUTAMIC ACID and its esters and salts have a tendency to form α-pyrrolidone derivatives1 by lactam formation:  The cyclization can be brought about by heating. A strong catalytic effect of ammonia has been recorded2.
The cyclization can be brought about by heating. A strong catalytic effect of ammonia has been recorded2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foreman, F. W., Biochem. J., 8, 484 (1914). Abderhalden, E., and Kautzsch, K., Z. physiol. Chem., 64, 452 (1910). Fischer, E., and Boehner, R., Chem. Ber., 44, 1332 (1911). Abderhalden, E., and Weil, A., Z. physiol. Chem., 74, 459 (1911).
Coleman, D., J. Chem. Soc., 2294 (1951).
Frankel, M., and Katchalski, E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 65, 1670 (1943). Bailey, J. L., Nature, 164, 889 (1949). Khurgin, Y. J., Poroshin, K. T., and Kozarenko, T. D., Izvestia Acad. Nauk S.S.S.R., (Chem.), 174 (1957).
Doty, P., and Lundberg, R. D., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 78, 4810 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HUBERT, A., BUIJLE, R. & HARGITAY, B. Carbon Dioxide Catalysis of the Formation of Pyroglutamic Acid. Nature 182, 259 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/182259a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/182259a0