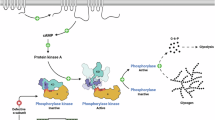
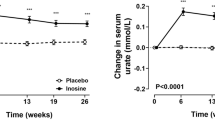
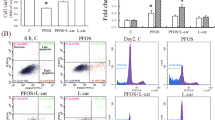
Abstract
UNDER the above title Goodall1 showed that a mixture of carnosine di- and mono-phosphates has a relaxing action practically identical with that of creatine phosphate on the glycerol-extracted muscle fibre. He raised the question of the presence and role of this substance in muscle, and pointed out that its non-detection so far may be because it is so much more acid-labile than creatine phosphate1,2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodall, M. C., Nature, 178, 539 (1956).
Severin, S. E., Georgievskaya, E. F., and Ivanov, V. I., Biokhimia, 12, 35 (1948).
Fleckenstein, A., Janke, J., Davies, R. E., and Krebs, H. A., Nature, 174, 1081 (1954).
Mommaerts, W. F. H. M., Nature, 174, 1083 (1954).
Fleckenstein, A., Janke, J., and Davies, R. E., Arch. Exp. Path. u. Pharmakol., 228, 596 (1956).
Chance, B., and Connelly, C. M., Nature, 179, 1235 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CAIN, D., DELLUVA, A. & DAVIES, R. Carnosine Phosphate as Phosphate Donor in Muscular Contraction. Nature 182, 720–721 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1038/182720a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/182720a0