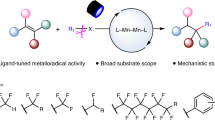
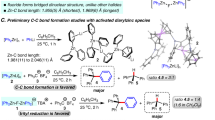
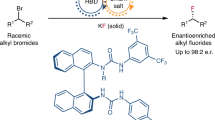
Abstract
THE attenuation of microwaves by flames containing traces of alkali metals may be used to determine the electron concentration, arising from the ionization of the alkali, in these flames1,2. If a halogen is added to such a flame, the electron concentration is reduced directly by the formation of negative ions, and indirectly by the formation of the alkali halide3,4. Flame photometric studies show that the halogens also reduce the excess hydrogen atom concentration in the flame5; but it has been observed that fluorine has the least effect6. This reduction makes it difficult to estimate the bond energies of the alkali halides from microwave studies7, because of the indirect nature of the arguments used in the estimations8. In the case of fluorine, however, the argument is simplified by the unimportance of the negative ion effect, since the electron affinity of fluorine is low relative to the bond energies of the alkali fluorides, and by the much smaller disturbance produced in the hydrogen atom concentration. In addition, the observations are made at high temperatures where the hydrogen atom concentration approaches equilibrium5 and it is possible to obtain reliable and consistent results, which it is of interest to place on record.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belcher and Sugden, Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 201, 480; 202, 17 (1950).
Smith and Sugden, Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 211, 31, 52 (1952).
Page, Disc. Farad. Soc., 19, 87 (1955).
Sugden, Disc. Farad. Soc., 19, 68 (1955).
Bulewicz, James and Sugden, Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 227, 312 (1958).
Bulewicz and Page (unpublished work).
Page, thesis (Cambridge, 1955).
Page and Sugden (to be published).
Cottrell, “The Strengths of Chemical Bonds” (Butterworths, London, 1954).
Smith and Sugden, Proc. Roy. Soc., A. 219, 204 (1953).
Gaydon, “Dissociation Energies—Spectra of Diatomic Molecules” (London, 1957).
Barrow and Caunt, Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 219, 120 (1953).
Bulewicz and Sugden (to be published).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PAGE, F., SUGDEN, T. Bond Energies of Some Alkali Fluorides. Nature 183, 1672 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1038/1831672a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1831672a0