Abstract
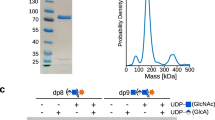
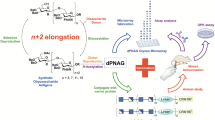
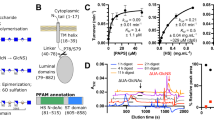
TYPE XIV Pneumococcus polysaccharide, which contains N-acetyl glucosamine, glucose and galactose residues1, has been methylated using dimethyl sulphate and sodium hydroxide (Haworth method2) to yield a methyl ether (I) which on hydrolysis gave 3-O-methyl D-glucosamine as the only methylated hexosamine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, Heidelberger, Stacey, and Tipper, J. Chem. Soc., 3468 (1958).
Haworth, J. Chem. Soc., 107, 8 (1915).
Freudenberg and Boppel, Ber., 71, 2505 (1938).
Orr and Harris, Nature, 169, 544 (1952).
Roseman and Ludowieg, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 76, 301 (1954).
Zilliken, Brown, Rose and György, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 54, 392 (1955).
Fried and Stavely, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 74, 5461 (1952).
Fried and Walz, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 74, 5468 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BARKER, S., STACEY, M. & TIPPER, D. N-Methylation of Methyl 2-Acetamido-2-Deoxy-α-D-Glucopyranoside. Nature 184, 1718 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1038/1841718a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1841718a0
This article is cited by
-
Lactaminic acid content of human milk
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (1971)