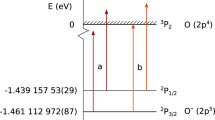
Abstract
WE have reported recently the results of a series of measurements of the electron loss cross-section for hydrogen atoms of 5–40 keV. energy in various gases1,2. The method employed is capable of some precision, and the cross-sections obtained are accurate, we believe, to within 2–3 per cent. As a result we have been able to determine that in hydrogen and in carbon monoxide the cross-section does not vary smoothly with energy, but has a number of large fluctuations. In the carbon monoxide cross-section, for example, there are nine maxima in the region 8–40 keV. The magnitude of the oscillations is of the order of 10−16 cm.2 in a total cross-section of the order of 1–5 × 10−16 cm.2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curran, R., and Donahue, T. M., Phys. Rev. (to be published); Bull. Amer. Phys. Soc., Ser. II, 4, 234 (1958).
Donahue, T. M., and Hushfar, F., Phys. Rev. Letters, 3, 470 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DONAHUE, T., HUSHFAR, F. Detection of Negative Ions formed by Charge Transfer. Nature 186, 1038–1039 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/1861038a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1861038a0