Abstract
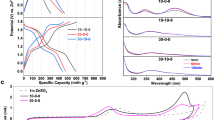
IN a recent communication, Mr. S. V. Subrahmaniam1 has reported measurements of ultrasonic velocities in aqueous solutions of cadmium iodide and mercuric chloride. I have made a detailed investigation of the variation of ultrasonic velocities in a number of aqueous solutions of electrolytes with concentration and temperature. The electrolytes that show the rather unusual behaviour of decreasing sound velocity with increasing concentration are the following: (1) cadmium bromide, (2) cadmium iodide, (3) zinc iodide, (4) strontium iodide, (5) lead acetate, (6) uranyl chloride, and (7) uranyl nitrate. The detailed results were published2,3; the conclusions reached in those studies are as follows :
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Subrahmaniam, S. V., Nature, 185, 371 (1960).
Balachandran, C. G., J. Indian Inst. Sci., 37, 27 (1955).
Balachandran, C. G., J. Indian Inst. Sci., 38, 1 (1956).
Barthel, R., J. Acous. Soc. Amer., 26, 227 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BALACHANDRAN, C. Ultrasonic Velocities in Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions. Nature 187, 136–137 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/187136a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/187136a0
This article is cited by
-
Ultrasonic Velocity in Aqueous Solutions of Some Electrolytes
Nature (1961)
-
Ultrasonic Velocity in Aqueous Silver Nitrate Solution
Nature (1961)