Abstract
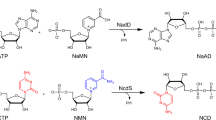
NICOTINIC acid nucleotide (5′-phospho-β-D-ribofuranosylpyridinium-3-carboxylate) and its adenylyl derivative, adenine-nicotinic acid dinucleotide, have recently been identified as intermediates in the biosynthesis of pyridine nucleotide coenzymes1. These compounds have been found in fungi2,3, and the mononucleotide has been isolated in small amounts from yeast4. Both nucleotides have also been obtained in very low yields by enzymic modification of adenine-nicotinamide dinucleotide (coenzyme I)2,3,5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Preiss, J., and Handler, P., J. Biol. Chem., 233, 488, 493 (1958).
Serlupi-Crescenzi, G., and Ballio, A., Nature, 180, 1203 (1957).
Ballio, A., and Russi, S., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 85, 567 (1959).
Wheat, R. W., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 82, 83 (1959).
Lamborg, M., Stolzenbach, F. E., and Kaplan, N. O., J. Biol. Chem., 231, 685 (1958).
Dox, A. W., “Organic Syntheses”, edit. by Gilman, H., and Blatt, A. H., second ed., 1, 266 (John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ATKINSON, M., MORTON, R. Synthesis of Nicotinic Acid Nucleotides. Nature 188, 58 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/188058b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/188058b0