Abstract
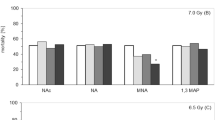
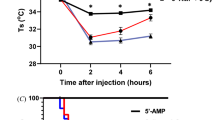
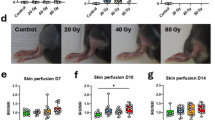
S,β-AminoethyUsothiuronium.Br.HBr (AET) is of known value in mice, and given parenterally in an appropriate dose will convert a LD 100/30 dose of whole-body X-radiation to essentially a LD)0/30 (ref. 1). The oral administration of AET prior to X-radiation is said to be effective (ref. 2 and Doherty, D. G., personal communication), but no definite results have yet been published. Oral cysteamine has been reported to be effective in both mice and rats with a longer duration of action than intraperitoneal injection3, but this has been disputed4.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doherty, D. G., and Burnett, jun., W. T., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 89, 312 (1955).
Hollaender, A., Proc. Int. Conf. Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy, 16 (Geneva, 1955).
Bacq, Z. M., Proc. Int. Conf. Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy, 11 (Geneva, 1955).
Langendorff, H., Koch, R., and Hagen, U., Strahlentherapie, 95, 238 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DACQUISTO, M., BLACKBURN, E. Protective Effect of orally administered S,β-Aminoethylisothiuronium.Br.HBr against X-radiation Death in Mice. Nature 190, 270 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1038/190270a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/190270a0