Abstract
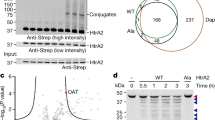
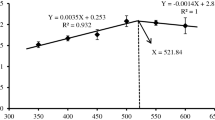
RECENTLY we have described an enzyme system which catalyses the exchange of the amide group of protein-bound glutamine with primary amines, such as methylamine, putrescine, histamine, serotonin, etc., and also hydroxylamine and ammonia1. The livers of rodents, and in particular of guinea pigs, are potent sources of the enzyme. This calcium-dependent enzyme not only catalyses the exchange with primary amines but also the hydrolysis of the amide group of protein-bound glutamine2. In the absence of added amine the ɛ-amino group of protein-bound lysine may act as the replacing agent3. The enzyme was named ‘transglutaminase’. All mammalian organs examined, and in particular liver and brain, contain proteins which may act in vitro as amine-accepting substrates, as are also a number of purified proteins, such as casein, lactoglobulin, insulin, pepsin, etc.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke, D. D., Neidle, A., Sarkar, N. K., and Waelsch, H., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 71, 277 (1957). Clarke, D. D., Mycek, M. J., Neidle, A., and Waelsch, H., ibid., 79, 338 (1959). Mycek, M. J., Clarke, D. D., Neidle, A., and Waelsch, H., ibid., 84, 528 (1959).
Mycek, M. J., and Waelsch, H., J. Biol. Chem., 235, 3513 (1960).
Neidle, A., Mycek, M. J., Clarke, D. D., and Waelsch, H., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 77, 227 (1958).
The increase of histidine decarboxylase in the skin and lung of rodents after administration of B. pertussis vaccine and under various stress situations has heen reported (cf. Schayer, R. W., Science, 131, 226 (1960)).
Shore, P. A., Burkhalter, A., and Cohn, jun., V. H., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 127, 182 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WAJDA, I., GINSBURG, M. & WAELSCH, H. Incorporation of Histamine into Liver Protein in vivo. Nature 191, 1204–1205 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1038/1911204a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1911204a0
This article is cited by
-
Protein Modifications catalysed by Transglutaminase
Nature (1963)