Abstract
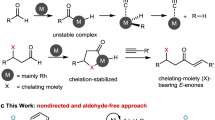
Kleiderer and Kornfeld1 converted cholesterol, a 3-hydroxy-Δ5-steroid, into Δ4-cholestenone by heating cholesterol in toluene solution with Raney nickel in presence of cyclohexanone as hydrogen acceptor. Later, Romo2 described the formation of 3-keto-Δ4-steroids from the 3-hydroxy-Δ4-steroids by the action of the same catalyst in presence of acetone or methyl ethyl ketone as hydrogen acceptor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleiderer, E. C., and Kornfeld, E. C., J. Org. Chem., 13, 455 (1948).
Romo, J., Bol. inst. quim. univ. nacl. auton. (Mexico), 4, 91 (1952).
Chakravarti, R. N., and Robinson, R., J. Chem. Soc., 78 (1947).
Chakravarti, D., Chakravarti, R. N., and Mitra, M. N., Nature, 186, 236 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHAKRAVARTI, D., CHAKRAVARTI, R. & MITRA, M. Effect of Raney Nickel on A/B Ring Fusion of Steroids. Nature 193, 1071 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/1931071a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1931071a0