Abstract
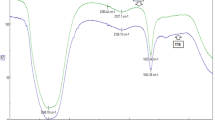
A BENZENE/ETHANOL (65 : 35) Soxhlet extract of air-dried high-moor peat (bitumen) has been separated into fractions by means of a column of the strongly basic anion-exchange resin ‘De-Acidite FF’ in the acetate form. The resin was converted from the chloride form in the manner described by Logie1. The effluent was collected in 2.5 gm. fractions and optical density measurements at 285 mµ were employed for the detection of the eluted fractions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Logie, D., Analyst, 82, 568 (1957).
Van Dijk, H., Sci. Proc. Roy. Dublin Soc., A, 1 (4), 163 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
THOMAS, J. Fractionation of Peat Bitumen by Anion-Exchange Chromatography. Nature 193, 975–976 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/193975b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/193975b0