Abstract
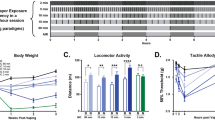
THIS communication concerns the vast difference in percutaneous absorption through human skin of two related substances, nicotinic acid and ethyl nicotinate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stoughton, R. B., Clendenning, W. E., and Kruse, D., J. Invest. Derm., 35, 337 (1960).
Treherne, J. E., J. Physiol. (Lond.), 133, 171 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CRONIN, E., STOUGHTON, R. Percutaneous Absorption of Nicotinic Acid and Ethyl Nicotinate in Human Skin. Nature 195, 1103–1104 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/1951103b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1951103b0
This article is cited by
-
Temperature and Concentration Effects on Penetration of N-Octylamine through Human Skin In Situ**From the Applied Physiology Branch, Physiology Department, Research Laboratories, Edge-wood Arsenal, Edgewood Arsenal, Maryland 21010.
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (1969)
-
Announcement
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (1967)
-
Topical Suppression of Eccrine Sweat Delivery with a New Anticholinergic Agent
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (1964)