Abstract
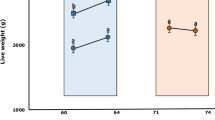
IN an earlier communication we reported that rats fed a diet containing 2 per cent of DL-α-guanidinopropionic acid (alacreatine) develop weakness during a 6-week period1. In subsequent work we have been unable to demonstrate either a defect in creatine metabolism in these animals or improvement of the weakness by creatine administration. Because of an odour which suggested the presence of a sulphur-containing compound in the alacreatine preparation further experiments were done with highly purified odourless alacreatine. None of the animals receiving the purified alacreatine became weak. It thus appears that the weakness was not caused by alacreatine, but by an impurity. The impurity has not been identified. However, various isothiourea and guanidine derivatives are known to be toxic in acute dose2 and such compounds could have been present in the original preparations of alacreatine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitch, C. D., and Dinning, J. S., Nature, 187, 421 (1960).
Guggenheim, M., Die biogenen Amine, 386 (S. Karger, Basel, 1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FITCH, C., DINNING, J. Effect of Alacreatine on the Rat. Nature 198, 1003 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/1981003a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1981003a0