Abstract
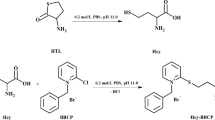
ISOVALTHINE crystals first isolated from urine were rhombic plates which gave DL-alanine after treatment with Raney nickel. Needle-shaped crystals were obtained by condensation of L-cysteine and (±)-α-bromoisovaleric acid. They were a mixture of L- and L-allo-isovalthine, and readily converted into the rhombic form by heating in hydrochloric acid1,2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mizuhara, S., and Ohmori, S., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 92, 53 (1961).
Ohmori, S., and Mizuhara, S., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 96, 179 (1962).
Ubuka, T., J. Biochem., 52, 440 (1962).
Tukutome, K., Acta Med. Okayama, 16, 241, 247 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OHMORI, S., UBUKA, T., KUWAKI, T. et al. Configuration of Urinary Isovalthine. Nature 200, 678–679 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/200678b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/200678b0