Abstract
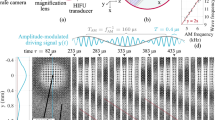
THE extensive measurements1 on the retardation of evaporation by monolayers conducted during the past decade at Columbia University have been restricted to static conditions to eliminate the erratic results arising from uncontrollable turbulence induced by a current of air passed over the surface of the water. We have extended these investigations by producing capillary waves of wave-length 0.5 cm, of frequency 60 c/s, and of amplitudes extending from 0.08 cm to 0.03 cm, by the action of a mechanical vibrator, that is, we have measured the effects of waves without the complication of wind.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
La Mer, V. K., Retardation of Evaporation by Monolayers (Academic Press, New York, 1961).
Davies, J. T., Chem. and Indust., 906 (1962).
MacArthur, I. K. H., Research, 15, 230 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LA MER, V., HEALY, T. Effects of mechanically produced Capillary Waves on the Evaporation of Water through Monolayers. Nature 201, 488 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1038/201488a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/201488a0
This article is cited by
-
Ultrahigh evaporative heat transfer measured locally in submicron water films
Scientific Reports (2022)