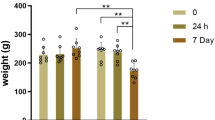
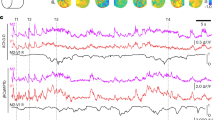
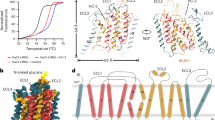
Abstract
THE presence of neurones in the cerebral cortex which are sensitive to acetylcholine has been well established1. The stable substance carbaminoyl choline (carbachol) is also effective2, and we have measured the uptake of carbaminoyl choline chloride (N-methyl-3H) in slices of cerebral cortex from the rat.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krnjević, K., and Phillis, J. W., J. Physiol., 166, 296 (1963).
Krnjević, K., and Phillis, J. W., J. Physiol., 166, 328 (1963).
McIlwain, H., and Rodnight, R., in Practical Neurochemistry (Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 1962).
Creese, R., Scholes, N. W., and Taylor, D. B., J. Pharmacol., 124, 47 (1958).
Creese, R., Taylor, D. B., and Tilton, B., J. Pharmacol., 138, 8 (1963).
Taylor, D. B., Creese, R., and Scholes, N. W., J. Pharmacol., 144, 293 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CREESE, R., TAYLOR, D. Effect of d-Tubocurarine on Uptake of Labelled Carbaminoyl Choline in Brain Slices of the Rat. Nature 206, 310 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/206310a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/206310a0