Abstract
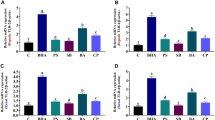
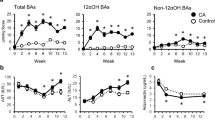
As reviewed by Fruton1, cathepsins are intracellular proteinases with acid pH optima, ubiquitously found in animal tissues. In the mammal, highest concentrations of cathepsins are found in liver, kidney and spleen2–4. However, perfused rat liver was found to catabolize only 13–15 per cent of the total albumin broken down in the whole animal5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fruton, J. S., in The Enzymes, 4, 223 (Academic Press, New York, 1960).
Tappel, A. L., Sawant, P., and Shibko, S., in Ciba Foundation Symposium on Lysosomes, 73 (Little and Brown, Boston, 1963).
Shibko, S., and Tappel, A. L., J. Cell. and Comp. Physiol., 61, 85 (1963).
Babson, A. L., Science, 123, 1082 (1956).
Cohen, S., and Gordon, A. H., Biochem. J., 70, 544 (1958).
Hsu, L., and Tappel, A. L., J. Cell. Biol., 23, 233 (1964).
Miller, G. L., Anal. Chem., 31, 964 (1959).
Friedberg, F., Tarver, H., and Greenberg, D., J. Biol. Chem., 173, 355 (1948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HSU, L., TAPPEL, A. Catheptic Activity of the Gastrointestinal Tract, Liver, Spleen and Kidney of the Rat. Nature 207, 1200 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/2071200a0
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2071200a0