Abstract
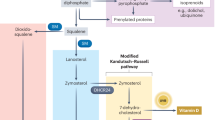
SYNTHESIS of the protein component of human low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and elaboration of these lipoproteins from lipid and protein constituents, are regarded as occurring in the liver1. In the Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome, absence of LDL is associated with steatorrhoea and changes in small-gut histology2. Salt et al.3 have speculated that the gut wall might be one site of lipoprotein synthesis. Isselbacher and Budz4 have shown that rat intestinal mucosa does synthesize lipoproteins. In rats, cholesterol synthesis occurs in the gut5. In human beings, 70 per cent of plasma cholesterol is carried by LDL, and if gut wall synthesis of cholesterol is shown to occur in man, the possibility again arises that a proportion of human LDL might also be elaborated in the intestinal mucosa. LDL newly synthesized by the gut could reach the general circulation via lacteal-lymphatic pathways, or directly through the portal venous system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cornwell, D. G., and Kruger, F. A., J. Lipid Res., 2, 110 (1961).
Isselbacher, K. J., Scheig, R., Plotkin, G. R., and Caulfield, J. B., Medicine (Baltimore), 43, 347 (1964).
Salt, H. B., Wolff, O. H., Lloyd, J. K., Fosbrooke, A. S., Cameron, A. H., and Hubble, D. V., Lancet, ii, 325 (1960).
Isselbacher, K. J., and Budz, D. M., Nature, 200, 364 (1963).
Fiegelson, E. B., Drake, J. W., and Recant, L., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 50, 437 (1957).
Soothill, J. F., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 59, 859 (1962).
Walton, K. W., and Scott, P. J., J. Clin. Path., 17, 627 (1964).
Scott, P. J., Dykes, P. W., Davies, J. L., Walton, K. W., in Biochemical Problems of Lipids, edit. by Frazer, A. C., 318 (Elsevier Publishing Co., Amsterdam, 1963).
Gitlin, D., Cornwell, D. G., Nakasato, D., Oncley, J. L., Hughes, W. L., and Janeway, C. A., J. Clin. Invest., 37, 172 (1958).
Walton, K. W., Scott, P. J., Dykes, P. W., and Davies, J. L., Clin. Sci. (submitted for publication).
Courtice, F. C., Woolley, G., and Garlick, D. G., Austral. J. Exp. Biol. and Med. Sci., 40, 111 (1962).
Matthews, C. M. E., Phys. in Med. Biol., 2, 36 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SCOTT, P., WINTERBOURN, C. Role of the Gut in Synthesizing the Protein Component of Low-density (Beta) Lipoprotein. Nature 208, 494–495 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/208494a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/208494a0