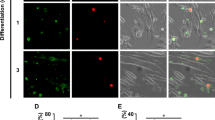
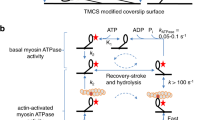
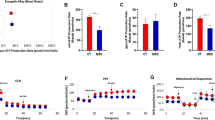
Abstract
DEUTERIUM oxide is known to retard the contraction of living muscle1–3. The site of its action, however, remains obscure; it affects significantly neither the membrane excitation4–6 nor the contraction of the proteins in glycerol-extracted muscle5. Deuterium oxide has, however, a differential effect on the contractile response to a number of nucleotides; whereas the interactions with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and cytodine triphosphate (CTP) are not affected, those with inosine triphosphate (ITP) and uridine triposphate (UTP) are retarded5. The ATPase of myofibrils6 and myosin B7 is reduced by deuterium oxide under certain conditions; at neutral pH the myosin B ATPase is, however, not significantly affected7. In the case of ITPase, the reaction is always slower on substitution of deuterium oxide for normal water (H2O) (ref. 7).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, T. C., and Warren, J., Science, 81, 346 (1935).
Brandt, W., Klin. Wschr., 14, 1597 (1935).
Verzar, F., and Haffter, C., Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol., 236, 714 (1935).
Goodall, M. C., Nature, 182, 677 (1958).
Kaminer, B., Nature, 185, 172 (1960).
Svensmark, O., Acta Physiol. Scand., 53, 75 (1961).
Hotta, K., and Morales, M. F., J. Biol. Chem., 235, PC 61 (1960).
Bozler, E., Amer. J. Physiol., 168, 760 (1952).
Bendall, J. R., J. Physiol., 121, 232 (1953).
Szent-Györgyi, A., Biol. Bull., 96, 140 (1949).
Glascoe, P. K., and Long, F. A., J. Phys. Chem., 64, 188 (1960).
Lorand, L., Molnar, J., and Moss, C., Conf. Biochem. Muscular Contraction, Tokyo, 85 (1957).
Baird, G. D., and Perry, S. V., Biochem. J., 77, 262 (1960).
Kaminer, B., Arch. Biochem. Biophys. (in the press).
Wiberg, K. B., Chem. Rev., 55, 713 (1955).
Kritchevsky, D., and Katz, J. J., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 84, 573 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KAMINER, B. Effect of Deuterium Oxide on the Relaxation of Glycerol-extracted Muscle. Nature 209, 809–810 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/209809a0
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/209809a0