Abstract
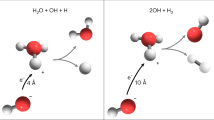
WHEN water vapour is irradiated, the main primary positive ion is H2O+ and it may be assumed that the reaction:  (k1 = 1.26 × 10−9 cm3 molecules−1 sec−1) will result in the formation of hydronium ions1. It has been suggested2,3 that neutralization of the hydronium ion by recombination with electrons can lead to the formation of two hydrogen atoms per ion:
(k1 = 1.26 × 10−9 cm3 molecules−1 sec−1) will result in the formation of hydronium ions1. It has been suggested2,3 that neutralization of the hydronium ion by recombination with electrons can lead to the formation of two hydrogen atoms per ion:  but there has been no evidence available to decide between this process and the alternative:
but there has been no evidence available to decide between this process and the alternative:  giving one hydrogen atom per ion. In an investigation of the radiolysis of mixtures of deuterium oxide and propane, we have obtained results which have a bearing on this question.
giving one hydrogen atom per ion. In an investigation of the radiolysis of mixtures of deuterium oxide and propane, we have obtained results which have a bearing on this question.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lampe, F. W., Field, F. H., and Franklin, N. L., J. Amer. Chem. Soc, 79, 6132 (1957).
Hart, E. J., and Piatzman, R. L., in Mechanisms in Radiobiology, 1, 176 (Academic Press Inc., 1961).
Fiquet-Fayard, F., J. Chim. Phys., 57, 453 (1960).
Baxendale, J. H., and Gilbert, G. P., Faraday Soc. Disc, 36, 186 (1963).
Baxendale, J. H., and Gilbert, G. P., J. Amer. Chem. Soc, 86, 576 (1964).
Field, F. H., and Lampe, F. W., J. Amer. Chem. Soc, 80, 5587 (1958).
Ausloos, P., and Gorden, R., J. Chem. Phys., 41, 1278 (1964).
Tal'Roze, V. L., and Frankevich, E. L., Dokl. Akad. Nauk S.S.S.R., 86, 909 (1952).
Munson, M. S. B., and Field, F. H., J. Amer. Chem. Soc, 87, 4242 (1965).
Kebarle, P., and Hogg, A. M., J. Chem. Phys., 42, 789 (1965).
Meisels, G. G., J. Chem. Phys., 41, 51 (1964).
Johnson, G. R. A., and Warman, J. M., Trans. Faraday Soc, 61, 1709 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JOHNSON, G., SIMIC, M. Neutralization of Hydronium Ions in the Radiolysis of Water Vapour. Nature 210, 1356–1357 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/2101356b0
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2101356b0