Abstract
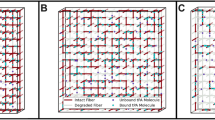
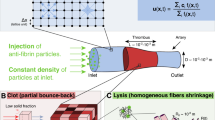
RECENTLY I reported1 lysis of thrombi in the veins and arteries of animals with sodium gluconate and a dialysable constituent of fibrin extract or whole blood. The ultraviolet absorption spectrum of fibrin extract displayed a maximum at 275 mµ and a minimum at 247 mµ. These values happen to coincide closely with those recorded for tyrosine. This finding suggested that L-tyrosine might be successfully substituted for fibrin extract and, if this was so, that a peptide formed from the amino-acid and gluconic acid would also be fibrinolytic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopper, P. H., Nature, 211, 43 (1966).
Iacobellis, M., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 59, 199 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOPPER, P. Rapid Induction of in vivo Fibrinolysis with D-Gluconyl-L-tyrosine. Nature 211, 1417 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/2111417a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2111417a0
This article is cited by
-
Physiological activities of gluconyl peptides
Experientia (1967)