Abstract
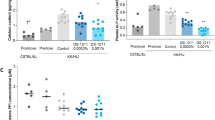
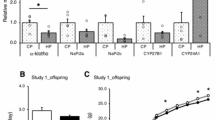
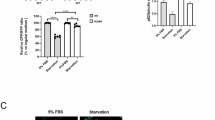
DURING the development of the mouse, alkaline phosphatase activity in the duodenum rises sharply before birth, falls back slightly, and then increases twenty-fold or more between 15 and 20 days1. This second rise is accelerated rather than retarded by inhibitors of RNA and protein synthesis2,3. Injection of actinomycin D, an inhibitor of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis4, into 9-day-old mice more than doubles their phosphatase activity within a 54 h period3, and the enhanced activity shows the normal increased preference for phenylphosphate over beta-glycerophosphate. Because these effects were obtained at a period of development when a considerable amount of phosphatase activity is already present, we thought it would be interesting to investigate the effect of actinomycin at a time when phosphatase activity first appears.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moog, F., J. Exp. Zool., 118, 187 (1951).
Moog, F., Science, 144, 414 (1964).
Moog, F., Adv. Enzyme Regulation, 3, 221 (1965).
Reich, E., and Goldberg, I. H., in Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. and Mol. Biol., 3, 183 (1964).
Moog, F., J. Exp. Zool., 115, 109 (1950).
Hinni, J. B., and Watterson, R. L., J. Morph., 113, 381 (1963).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J., J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265 (1951).
Kato, Y., Devel. Biol., 1, 477 (1959).
Moog, F., Vire, H. R., and Grey, R. D., Biochim. Biophys. Acta (in the press).
Simpson, G. G., Roe, A., and Lewontin, R. C., Quantitative Zoology (Harcourt, Brace and Co., New York, 1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GREY, R., MOOG, F. Elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity in the Intestine of the Chick Embryo by Actinomycin D. Nature 211, 418–419 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/211418b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/211418b0