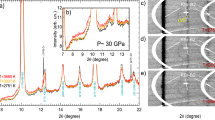
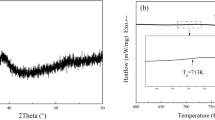
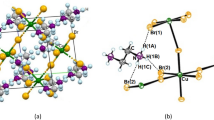
Abstract
MURRAY1 has predicted that crystalline cuprous chloride may be of use as a modulator material in lasers. Crystals of this material are generally grown from the melt2, but the method has certain disadvantages. First, the presence of a phase transition2 15° C below the melting point (422° C) produces strains in the resulting crystals. This is further intensified by temperature gradients produced in the crystal during cooling from the melting point to room temperature. Contamination from container materials is another hazard. We have endeavoured to eliminate these undesirable influences by growing cuprous chloride at room temperature with a variation of the gel growth technique.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murray, L. A., Electron. Indust., 23 (No. 2), 83 (1964).
Sterzer, F., Blattner, D., and Miniter, S., J. Opt. Soc. Amer., 54, 62 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'CONNOR, J., DIPIETRO, M., ARMINGTON, A. et al. Gel Growth of Crystalline Cuprous Chloride. Nature 212, 68 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/212068a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/212068a0
This article is cited by
-
Kinetic study for the formation of microcrystalline “disks” of204T1I in gelatin medium
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry (1997)
-
Kinetic study on crystal growth in gels by radioisotopic labelling
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry Letters (1993)
-
Crystal growth in gel media
Bulletin of Materials Science (1982)
-
Calcification and the Ground Substance: Precipitation of Calcium Phosphate Crystals from a Nutrient Gel
Nature (1970)
-
Growth of Single Crystals of Silver Halides in Silica Gels at Near Ambient Temperatures
Nature (1967)