Abstract
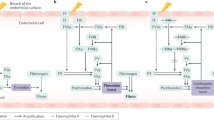
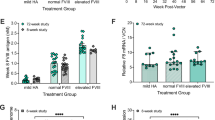
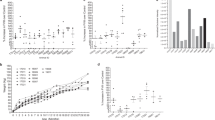
IT has been known for many years that patients with classic haemophilia bleed because they lack a plasma factor required for normal blood coagulation. This factor, factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor) of normal plasma, has been extensively investigated, but its exact site of origin is unknown. Recent developments in organ transplantation have stimulated us to look for the specific organ source of this procoagulant. If the site of synthesis of factor VIII could be identified, permanent replacement of the deficient factor in haemophilia might be possible. In the past, a variety of experimental approaches has been used to investigate the body's mechanisms for maintaining haemostatic levels of factor VIII: organ ablation1, total body irradiation2, administration of hepatotoxins3,4, reticulo-endothelial blockade5, physical exercise6, hormone administration7, and thromboplastin injections4. Several recent investigations have suggested that the spleen may play a part in the regulation of concentrations of factor VIII in the plasma of normal individuals. Weaver et al. demonstrated that factor VIII is maintained at normal concentrations when intact normal dogs are crosscirculated with haemophilic dogs, but that the concentrations decrease if a splenectomy is first performed on the normal animals8. In humans, Libre et al.9 have observed that splenectomy abolishes the rise in factor VIII that is known to follow injection of adrenaline into normal subjects10. Pool was able to recover antihaemophilic activity in extracts of splenic tissue, but not from a variety of other tissues11.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gross, J. D., Hartmann, R. C., Graham, J. B., and Taylor, C. B., Johns Hopkins Hosp. Bull., 100, 223 (1957).
Penick, G. D., Cronkite, E. P., Godwin, I. D., and Brinkhous, K. M., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 78, 732 (1951).
Graham, J. B., Collins, jun., D. J., Godwin, I. D., and Brinkhous, K. M., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 77, 294 (1951).
Penick, G. D., Roberts, H. R., Webster, W. P., and Brinkhous, K. M., Arch. Path., 66, 708 (1958).
Gaynor, E., and Spaet, T. H., Blood, 28, 595 (1965).
Rizza, C. R., J. Physiol., 156, 128 (1961).
Penick, G. D., in The Hemophilias (edit. by Brinkhous, K. M.), 251 (University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, 1964).
Weaver, R. A., Price, R. E., and Langdell, R. D., Amer. J. Physiol., 206, 335 (1964).
Libre, E. P., Cowan, D. H., and Shulman, N. R., Blood, 26, 890 (1965).
Ingram, G. I. C., J. Physiol., 156, 217 (1961).
Pool, J. G., Fed. Proc., 25, 317 abst. 719 (1966).
Graham, J. B., Buckwalter, J. A., Hartley, L. J., and Brinkhous, K. M., J. Exp. Med., 90, 97 (1949).
Langdell, R. D., Wagner, R. H., and Brinkhous, K. M., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 41, 637 (1953).
Holemans, R., Johnston, J. G., and Reddick, R. L., Nature, 208, 291 (1965).
Straub, P. W., Riedler, G., and Meili, E. O., Schweiz. Med. Wochschr., 96, 1199(1966).
Penick, G. D., Avarette, jun., H. E., Peters, R. M., and Brinkhous, K. M., Thromb. Diath. Haem., 2, 218 (1958).
Pool, J. G., and Spaet, T. H., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 87, 54 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WEBSTER, W., REDDICK, R., ROBERTS, H. et al. Release of Factor VIII (Antihaemophilic Factor) from Perfused Organs and Tissues. Nature 213, 1146–1147 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2131146a0
Received:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2131146a0
This article is cited by
-
Factor VIII-related antigen in tissues detected by the indirect immunofluorescence technique
Blut Zeitschrift für die Gesamte Blutforschung (1974)
-
Factor VIII on the Vascular Intima: Possible Importance in Haemostasis and Thrombosis
Nature New Biology (1973)