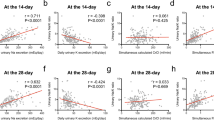
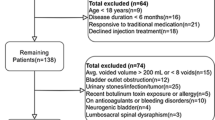
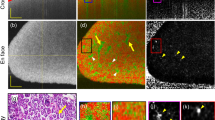
Abstract
NATURAL thunder—a playback of recorded thunder—with a predominant frequency of 150 c/s at an intensity of 98–100 dB has caused diuresis and increased urinary outputs of sodium and potassium in rats1. These responses were similar to those caused by subcutaneous injections of 4.0 mU of oxytocin and the results of all investigations indicated that these urinary responses to low frequency sound were caused by the release of oxytocin1. The purpose of this communication is to report direct confirmation of these indications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogle, C. W., and Lockett, M. F., J. Endocrinol., 36, 281 (1966).
van Dongen, C. G., and Hays, R. L., J. Anim. Sci., 23, 1229 (1964).
van Dongen, C. G., and Hays, R. L., Endocrinology, 78, 1 (1966).
Burhoe, S. O., J. Hered., 31, 445 (1940).
Armstrong, D., Keele, C. A., Jepson, J. B., and Stewart, J. W., Nature, 174, 791 (1954).
van Dyke, H. B., Chow, B. F., Greep, R. O., and Rothen, A., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 74, 190 (1942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OGLE, C. Low Frequency Sound and Oxytocic Activity of Plasma in Rats. Nature 214, 1112–1113 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2141112a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2141112a0