Abstract
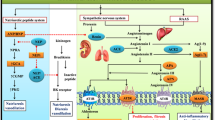
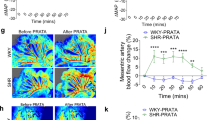
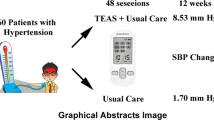
A NON-DIALYSABLE hypertensive substance stable to heat is found in rat serum after incubation at 37° C (refs. 1 and 2). The same activity can be demonstrated in the serum and plasma of human beings, pigs and rabbits, but not of frogs3. The blood pressure response to this active pressor principle (APP) was demonstrated in rats during an infusion of hypotonic glucose and compared with the hypertensive effect of synthetic angiotensin1. Because APP seems to be different from known hypertensive polypeptides and renin1, further purification of it is of interest.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kenner, Th., and Waldhäusl, W., Nature, 204, 581 (1964).
Khairallah, P. A., and Page, I. H., Amer. J. Physiol., 119, 341 (1960).
Waldhäusl, W., and Kenner, Th., Med. Pharmacol. Exp., 12, 388 (1965).
Croxatto, H., in Perspectives in Biology (edit. by Cori, C. F., Foglia, V. G., Leloir, L. F., and Ochoa, S.) (Elsevier, 1963).
Kenner, Th., and Waldhäusl, W., Zschr. Kreislauffschg., 54, 1143 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PETERLIK, M., WALDHÄUSL, W. Isolation of a Non-dialysable Active Pressor Principle from Pig Serum. Nature 214, 279 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/214279a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/214279a0
This article is cited by
-
Some properties of a high molecular vasopressor substance generated in human Serum by incubation
Basic Research in Cardiology (1978)