Abstract
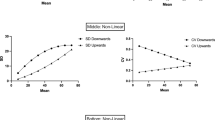
IT is accepted that the discharge of muscle spindle receptors is reduced or abolished during extrafusal contraction caused by unloading1,2. Acceleration of spindle receptor discharge which may occur during the early phase of muscle contraction on stimulation of the muscle nerve, ventral roots or supraspinal structures, however, has been considered to result not from contraction of intrafusal muscle fibres (active factor) but from pull of spindles induced by extrafusal contraction (passive factor)3–5. Stimulation of Deiters nucleus in the cat has been shown to result in simultaneous excitation of muscle spindle receptors and extrafusal muscle fibres in the gastrocnemius muscle6. The question is whether this acceleration of spindle discharge is caused by intrafusal contraction or mechanical deformations caused by extrafusal contraction. The experiments reported here concern the dissociation of passive from active factors by the use of a new finding, namely, the much longer binding of gallamine to intrafusal than extrafusal neuromuscular junctions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fulton, J. F., and Pi-Suñer, J., Amer. J. Physiol., 83, 554 (1928).
Matthews, B. H. C., J. Physiol., 78, 1 (1933).
Hunt, C. C., and Kuffler, S. W., J. Physiol., 113, 298 (1951).
Hunt, C. C., and Perl, E. R., Physiol. Rev., 40, 541 (1960).
Harvey, R. J., and Matthews, P. B. C., J. Physiol., 156, 470 (1961).
Carli, F., Diete-Spiff, K., and Pompeiano, O., Experientia, 22, 583 (1966).
Granit, R., Homma, S., and Matthews, P. B. C., Acta Physiol. Scand., 46, 185 (1959).
Granit, R., Pompeiano, O., and Waltman, B., J. Physiol., 147, 385 (1959).
Bessou, P., Emonet-Denand, F., and Laporte, Y., J. Physiol., 180, 649 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CARLI, G., DIETE-SPIFF, K. & POMPEIANO, O. Active and Passive Factors in Muscle Spindle Excitation. Nature 214, 838–839 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/214838a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/214838a0