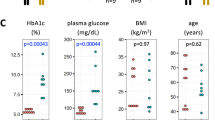
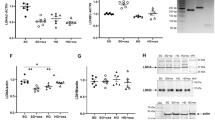
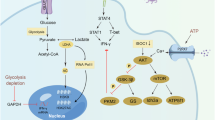
Abstract
THERE are some indications that diabetes mellitus is a disease involving a disorder of carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism. Leucocytes possess a nucleus and mitochondria, and metabolize glucose, amino-acids and fatty acids, and therefore might be useful for the investigation of certain aspects of metabolism in human diabetes. Investigation of glucose uptake and oxidation, lipid metabolism and lactic acid formation in leucocytes has had varied results1–3. Protein synthesis has not been investigated in leucocytes, and we aimed to determine the differences in protein metabolism in leucocytes from control and diabetic patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engelhardt, A., and Jahnke, K., Klin. Wschr., 42, 1147 (1964).
Awai, K., Hammarstrand, K., and Hennes, A. R., Metabolism, 13, 328 (1964).
Munroe, J., and Shipp, J., Diabetes, 14, 584 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
TOKODI, I., POZSÁR, B. Protein Synthesis in Leucocytes of Diabetic and Normal Subjects. Nature 215, 300–301 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/215300a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/215300a0