Abstract
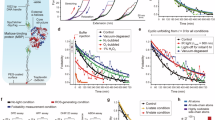
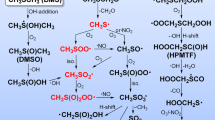
THE long-lived free radicals produced by gamma radiolysis of dry proteins at room temperature have been previously studied by electron spin resonance1 (ESR). The carbon radicals which can be observed by ESR have been interpreted2 as being predominantly located on glycine. Recently, the use of tritiated hydrogen sulphide as interceptor of free radicals has been proposed3 as a new experimental technique for determining the distribution of free radicals located on carbon atoms. The method in volves exposing the gamma irradiated lyophilized proteins to tritiated hydrogen sulphide in order to form carbon-tritium bonds in the protein. Tritium distribution among the amino-acids can be determined by subsequent hydrolysis, ammo-acid analysis and tritium counting; this measures the “secondary”1 free radical distribution. The terms “primary” and “secondary” free radicals refer, respectively, to (a) those radicals formed on irradiation at 77° K, and (b) those which arise from them on subsequent warming or which can be observed after radiolysis at room temperature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henriksen, T., Electron Spin Resonance and the Effects of Radiation on Biological Systems, 81 (National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., 1966).
Patten, R. A., and Gordy, W., Radiat. Res., 22, 29 (1964).
Riesz, P., White, jun., F. H., and Kon, H., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 88, 872 (1966); White, jun., F. H., Riesz, P., and Kon, H., Radiat. Res. (in the press).
Cottrell, T. L., The Strengths of Chemical Bonds, third ed. (Butterworth, London, 1958); Tedder, J. M., Quart. Rev., 14, 336 (1960).
Schuler, R. H., and Fessenden, R. W., Radiation Research, 99 (North–Holland, Amsterdam, 1967).
Hammond, K. R., and Householder, J. E., Introduction to the Statistical Method (Knopf, A. A., N. Y., 1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RIESZ, P., WHITE, F. Determination of Free Radicals in Gamma Irradiated Proteins. Nature 216, 1208–1210 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1038/2161208b0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2161208b0