Abstract
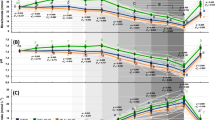
THERE is much evidence to suggest that the absorption of sodium and water by the small intestine depends on concomitant absorption of non-electrolytes. Thus, in man, jejunal absorption from isotonic saline is very slow, but the rate of absorption of both sodium and water is greatly increased by the addition of glucose to the intestinal lumen1,2. Galactose, but not fructose, has a similar effect on water absorption in man3. During the course of perfusion studies in man, we have found that bicarbonate ions have a stimulant effect on jejunal absorption of sodium and water and, furthermore, the magnitude of the effect on sodium is comparable with that of glucose.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schedl, H. P., and Clifton, J. A., Nature, 199, 1264 (1963).
Malawer, S. J., Ewton, M., Fordtran, J. S., and Ingelfinger, F. J., J. Clin. Invest., 44, 1072 (1965).
Holdsworth, C. D., and Dawson, A. M., Clin. Sci., 27, 371 (1964).
Cooper, H., Levitan, R., Fordtran, J. S., and Ingelfinger, F. J., Gastroenterology, 50, 1 (1966).
Fordtran, J. S., Gastroenterology, 51, 1089 (1966).
Hyden, S., Kungl. Landbrukshögskdans Annaler, 22, 139 (1955).
McHardy, G. J. R., and Parsons, D. S., Quart. J. Exp. Physiol., 42, 33 (1957).
Cooperstein, I. L., and Hogben, C. A. M., J. Gen. Physiol., 42, 461 (1959).
Funder, J., Ussing, H. H., and Wieth, J. O., Acta Physiol. Scand., 71, 65 (1967).
Fordtran, J. S., Fed. Proc., 26, 1405 (1967).
Wilson, T. H., Amer. J. Physiol., 187, 244 (1956).
Fisher, R. B., J. Physiol., 130, 655 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SLADEN, G., DAWSON, A. Effect of Bicarbonate on Sodium Absorption by the Human Jejunum. Nature 218, 267–268 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/218267a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/218267a0
This article is cited by
-
A novel mouse model of heatstroke accounting for ambient temperature and relative humidity
Journal of Intensive Care (2021)
-
The influence of buffer pH, glucose and sodium ion concentration on the acid microclimate in rat proximal jejunum in vitro
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1980)
-
Lactate and bicarbonate transport in rat and hamster jejuna incubated in vitro
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1980)
-
Water absorption and swelling in the rat small intestine in vitro
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1977)
-
Effect of intraluminal bicarbonate and chloride on fluid absorption by the rat renal proximal tubule
Kidney International (1976)