Abstract
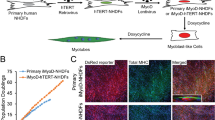
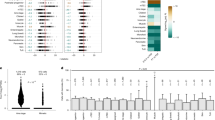
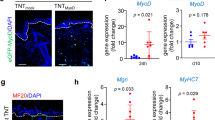
MYOID cells are a common constituent of the thymus in lower vertebrates. Many recent electron microscopic studies of amphibia, reptiles and birds1–8, as well as foetal mammals3,9, confirm the presence within these cells of all the principal components of skeletal muscle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van de Velde, R. L., and Friedman, N. B., Fed. Proc., 25, 661 (1966).
Van de Velde, R. L., and Friedman, N. B., J. Amer. Med. Assoc., 198, 287 (1966).
Van de Velde, R. L., and Friedman, N. B., Anat. Rec., 157, 392 (1967).
Strauss, A. J. L., Kemp, jun., P. J., and Douglas, S. D., Lancet, i, 772 (1966).
Raviola, E., and Raviola, G., Anat. Rec., 154, 483 (1966).
Raviola, E., and Raviola, G., Amer. J. Anat., 121, 623 (1967).
Bockman, D. E., and Winborn, W. B., J. Morphol., 121, 277 (1967).
Canaday, S. D., Anat. Rec. (in the press).
Mandel, T., Nature, 217, 276 (1968).
Henry, K., Lancet, i, 183 (1966).
Feltkamp-Vroom, T., Lancet, i, 1320 (1966).
Karnovsky, M. J., J. Cell. Biol., 27, 137A (1965).
Strauss, A. J. L., and Kemp, jun., P. G., J. Immunol., 99, 945 (1967).
Mackay, I. R., and Goldstein, G., Clin. Exp. Immunol., 2, 139 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOCKMAN, D. Myoid Cells in Adult Human Thymus. Nature 218, 286–287 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/218286a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/218286a0