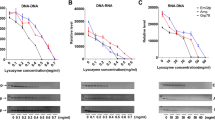
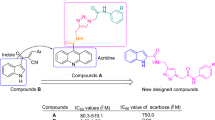
Abstract
THE structure and properties of hen's egg white lysozyme and of the lysozyme–inhibitor complexes are known in detail1,2, but there is no direct evidence as to which amino-acid residues are involved in the bond breaking step. Specific chemical modification of the active site residues is an obvious approach to the problem, arid we describe here an attempt to design specific inhibitors of lysozyme, using the affinity labelling principle3,4. Because the side chains of amino-acid residues Glu 35 and Asp 52 have been proposed as the catalytically active groups in lysozyme2, we have prepared potential lysozyme inhibitors which can react with carboxyl functions, and have investigated their effect on the enzyme.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, L. N., and Phillips, D. C., Nature, 206, 761 (1965).
Blake, C. C. F., Johnson, L. N., Mair, G. A., North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C., and Sarma, V. R., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 167, 378 (1967).
Wofsy, L., Metzger, H., and Singer, S. J., Biochemistry, 1, 1031 (1962).
Baker, B. R., Design of Active Site-Directed Irreversible Enzyme Inhibitors (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1967).
Rupley, J. A., Butler, L., Gerring, M., Hartdegen, F. J., and Pecoraro, R., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 57, 1088 (1967).
Dahlquist, F. W., Jao, L., and Raftery, M. A., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 56, 26 (1966).
Lehrer, S. S., and Fasman, G. D., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 23, 133 (1966).
Chipman, D. M., Grisaro, V., and Sharon, N., J. Biol. Chem., 242, 4388 (1967).
Ross, W. C. J., J. Chem. Soc., 2257 (1950).
Thomas, E. W., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 29, 628 (1967).
Sharon, N., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 167, 402 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
THOMAS, E., MCKELVY, J. & SHARON, N. Specific and Irreversible Inhibition of Lysozyme by 2′,3′-Epoxypropyl β-Glycosides of N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine Oligomers. Nature 222, 485–486 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1038/222485a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/222485a0
This article is cited by
-
The role of epoxide hydrolases in health and disease
Archives of Toxicology (2014)
-
Active site directed inhibitors and mechanism of action of glycosidases
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (1973)