Abstract
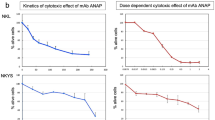
L5178Y lymphoma cells from DBA/2 mice grow well in vitro and the cytotoxicity of immune lymphoid cells can be assayed easily in terms of the degree to which they inhibit the growth of the lymphoma. Using this system we have already shown that sheep lymph cells, collected from the efferent ducts of individual lymph nodes that had been immunized with the lymphoma, displayed a powerful and immunologically specific cytotoxic action1. The cytotoxicity of the lymphoid cell population correlated with the percentage of large basophilic immunoblasts that were present and consequently an unequivocal cytotoxic action was only demonstrable between 4–7 days after immunization when large numbers of immunoblasts were present in the lymph. At later times the lymph was populated mainly with small lymphocytes and these cells, even when collected from hyperimmune sheep, were without demonstrable cytotoxic action in vitro. For these reasons it was concluded that the immunoblast was the cytotoxic cell. In these experiments the lymphoma cells were cultured in a medium containing 10 per cent heat-inactivated foetal calf serum.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denham, S., Hall, J. G., Wolf, A., and Alexander, P., Transplantation, 7, 194 (1969).
Thorbecke, G. J., Hochwald, G. M., van Furth, R., Müller-Eberhard, H. J., and Jacobson, E. B., in Complement (edit. by Wolstenholme, G. E. W., and Knight, J.) (Churchill, London, 1965).
Taylor, H. E., and Culling, C. F. A., Nature, 220, 506 (1968).
Perlmann, P., Perlmann, H., Müller-Eberhard, H. J., and Manni, J. A., Science, 163, 937 (1969).
Cunningham, A. J., Smith, J. B., and Mercer, E. H., J. Exp. Med., 124, 701 (1966).
Birbeck, M. S. C., and Hall, J. G., Nature, 214, 183 (1967).
Denham, S., Grant, C. K., Hall, J. G., and Alexander, P., Transplantation, 9, 366 (1970).
Brondz, B. D., Folia Biol., 10, 1 (1964).
Rosenau, W., and Morton, D. L., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 36, 825 (1966).
Brunner, K. T., Mauel, J., and Schindler, R., Immunology, 11, 499 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GRANT, C., DENHAM, S., HALL, J. et al. Antibody and Complement-like Factors in the Cytotoxic Action of Immune Lymphocytes. Nature 227, 509–510 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/227509a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/227509a0
This article is cited by
-
The immunological significance of cellular infiltrates in chronic rejection of human kidney transplants
Virchows Archiv A Pathological Anatomy and Histology (1975)