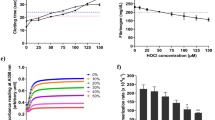
Abstract
THE conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, which is the last stage of the complex process of blood coagulation, is composed of three successive reactions1: an enzymatic hydrolysis by thrombin of four arginyl-lysyl bonds per molecule of fibrinogen, yielding a fibrin monomer; a spontaneous polymerization of monomers to form a gel or fibrin clot; and an enzymatic transamidation by fibrin stabilizing factor (factor XIII or fibrinase) between ε-amino groups of lysyl and glutaminyl side chains. The mechanism of the reversible polymerization of fibrin monomers remains largely unknown, although it can be studied separately because fibrin monomers can be stabilized in acidic media of high ionic strength such as 1 M NaBr, pH 5.32.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laki, K., and Gladner, J. A., Physiol. Rev., 44, 127 (1964).
Donnelly, T. H., Laskowski, M., Notley, N., and Scheraga, H. A., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 56, 362 (1955).
Sturtevant, J. M., Laskowski, jun., M., Donnelly, T. H., and Scheraga, H. A., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 77, 6168 (1955).
Endres, G. F., and Scheraga, H. A., Biochemistry, 7, 4219 (1968).
Stevens, C. L., and Lauffer, M. A., Biochemistry, 4, 31 (1965).
Josephs, R., and Harrington, W. F., Biochemistry, 7, 2834 (1968).
Blombäck, B., and Blombäck, M., Arkiv Kemi, 10, 415 (1956).
Ferry, J. D., and Morrisson, P. R., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 69, 388 (1947).
Kauzmann, W., Adv. Protein Chem., 14, 1 (1959).
Weber, G., and Laurence, D. J. R., Biochem. J., 56, 31 (1954).
Dodd, G. H., and Radda, G. K., Biochem. J., 114, 407 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COLLEN, D., VANDEREYCKEN, G. & DE MAEYER, L. Influence of Hydrostatic Pressure on the Reversible Polymerization of Fibrin Monomers. Nature 228, 669–671 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/228669a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/228669a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of supercritical Carbon Dioxide on proteins
Zeitschrift f�r Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung (1980)
-
Effect of temperature and pressure on polymerisation equilibrium of neuronal microtubules
Nature (1976)