Abstract
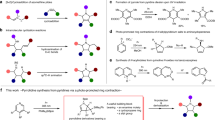
FOR the first time, some of the toxic effects of unsaturated pyrrolizidine alkaloids on rats have been reproduced by dosing animals with synthetic compounds. Many of the naturally occurring hepatotoxic alkaloids are esters of the isomeric amino-alcohols retronecine or heliotridine with various branched chain hydroxy-acids1. The most toxic alkaloids are cyclic diesters of retronecine1, which are particularly resistant to enzymic hydrolysis. Because hepatotoxicity of the pyrrolizidine alkaloids has been associated with the metabolic conversion of the pyrroline to a pyrrole ring2,3, with retention of the ester groups4, it was expected that simpler pyrroline esters would have similar toxic properties provided that the ester groups were resistant to enzymic hydrolysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoental, R., Israel. J. Med. Sci., 4, 1133 (1968).
Mattocks, A. R., Nature, 217, 723 (1968).
Culvenor, C. C. J., Downing, D. T., Edgar, J. A., and Jago, M. V., Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 163, 837 (1969).
Mattocks, A. R., and White, I. N. H., Nature New Biology, 231, 114 (1971).
Mattocks, A. R., and White, I. N. H., Anal. Biochem., 38, 529 (1970).
Davidson, J., J. Path. Bact., 40, 285 (1935).
Schoental, R., and Magee, P. N., J. Path. Bact., 74, 305 (1957).
Barnes, J. M., Magee, P. N., and Schoental, R., J. Path. Bact., 88, 521 (1964).
Mattocks, A. R., Nature, 228, 174 (1970).
Schoental, R., and Mattocks, A. R., Nature, 185, 842 (1960).
Mattocks, A. R., J. Chem. Soc. (C), 2698 (1969).
Baron, R. L., Casterline, J. L., and Orzel, R., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 9, 6 (1966).
Schoental, R., and Magee, P. N., J. Path. Bact., 78, 471 (1959).
Butler, W. H., Mattocks, A. R., and Barnes, J. M., J. Path., 100, 169 (1970).
McLean, E. K., Pharmacol. Rev., 22, 429 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MATTOCKS, A. Synthetic Compounds with Toxic Properties similar to those of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids and their Pyrrolic Metabolites. Nature 232, 476–477 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/232476a0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/232476a0