Abstract
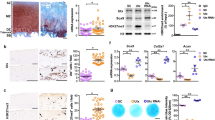
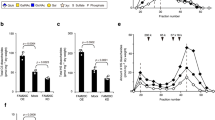
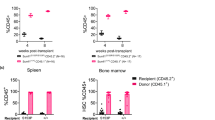
THE action of growth hormone (GH) on skeletal tissue was proposed to be mediated through a secondary substance, described by the operational term “sulphation factor”1. The observations underlying this hypothesis have been amply confirmed and extended. A GH-dependent plasma factor stimulates in cartilage not only the incorporation of sulphate into chondroitin sulphate, but also the incorporation of thymidine into DNA2, proline into the hydroxyproline of collagen3 and uridine into RNA4. GH has substantially no in vitro effect on cartilage metabolism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salmon, W. D., and Daughaday, W. H., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 49, 825 (1957).
Daughaday, W. H., and Reeder, C., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 68, 357 (1967).
Daughaday, W. H., and Mariz, I. K., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 59, 741 (1962).
Salmon, jun., W. D., and DuVall, M. R., Endocrinology, 86, 721 (1970).
Van Wyk, J. J., Hall, K., Van den Brande, J. L., and Weaver, R. P., J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 32, 389 (1971).
Van Wyk, J. J., Hall, K., Van den Brande, J. L., Weaver, R. P., Uthne, K., Hintz, R. L., Harrison, J. H., and Mathewson, P., Proc. Second Intern. Symp. Growth Hormone (edit. by Pecile, A., and Mueller, E.) (in the press).
Hall, K., and Uthne, K., Proc. Second Intern. Symp. Growth Hormone (edit. by Pecile, A., and Mueller, E.) (in the press).
Salmon, jun., W. D., and DuVall, M. R., Endocrinology, 87, 1168 (1970).
Jakob, A., Hauri, C., and Froesch, E. R., J. Clin. Invest., 47, 2678 (1968).
Raben, M. S., Murakawa, S., and Matute, M., Proc. Second Intern. Symp. Growth Hormone (edit. by Pecile, A., and Mueller, E.) (in the press).
Salmon, W. D., and Hosse, B. R., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 136, 805 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DAUGHADAY, W., HALL, K., RABEN, M. et al. Somatomedin: Proposed Designation for Sulphation Factor. Nature 235, 107 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1038/235107a0
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/235107a0
This article is cited by
-
Modulatory activity of testosterone on growth pattern and IGF-1 levels in vanishing testis syndrome: a case report during 15 years of follow-up
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2023)
-
Colostrogenesis: Role and Mechanism of the Bovine Fc Receptor of the Neonate (FcRn)
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2021)
-
The Actions of IGF-1 in the Growth Plate and Its Role in Postnatal Bone Elongation
Current Osteoporosis Reports (2020)
-
Growth hormone axis in patients with chronic kidney disease
Hormones (2019)
-
Possible effects of an early diagnosis and treatment in patients with growth hormone deficiency: the state of art
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017)