Abstract
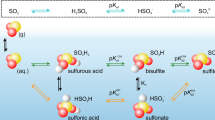
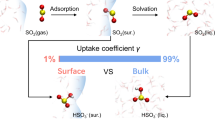
Liss1 has calculated the rate of exchange between sulphurdioxide and environmental water. We report here experimental work which verifies the results of his calculations. The rate of solution of SO2 at 20° C was examined by passing a nonlaminar flow of air (bulk velocity ∼1.5 cm s−1) and 35SO2 at concentrations around 300 µg m−3 over stirred sodium perchlorate solutions. The pH values of these solutions were adjusted by addition of sodium hydroxide or perchloric acid because ionic strength exerts little effect on rate of uptake. Oxidation of the sulphur (IV) anions in sodium perchlorate solution is small over the time scale involved (unpublished data of P. B.).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liss, P. S., Nature, 233, 327 (1971).
Danckwerts, P. V., Gas-Liquid Reactions, 145 (McGrawHill, London, 1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BRIMBLECOMBE, P., SPEDDING, D. Rate of Solution of Gaseous Sulphur Dioxide at Atmospheric Concentrations. Nature 236, 225 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1038/236225a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/236225a0
This article is cited by
-
Source apportionment of PM2.5 during different haze episodes by PMF and random forest method based on hourly measured atmospheric pollutant
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
Some considerations on the washout of sulfate from stack plumes
Water, Air, and Soil Pollution (1976)
-
Flux of Gases across the Air-Sea Interface
Nature (1974)