Abstract
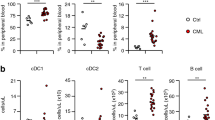
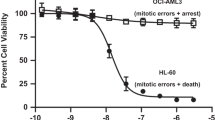
Flow cytometric expression of bcl-2 protein was analyzed in 90 newly diagnosed acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML) patients using an anti-bcl-2 monoclonal antibody by direct immunofluorescence technique and results were correlated with FAB cytotype, CD34 expression and clinical outcome. Bcl-2 was expressed in all AML cases with different intensity. The mean fluorescence index (MFI), expressed as the ratio of sample mean channel:control mean channel, ranged from 3.0 to 39.5 with a median value of 14. The MFI was significantly higher (P = 0.01) in M0 (20.9) and M1 (18.3) than in M2 (11.7), M3 (12.4), M4 (11.8) and M5 (9.5) cytotypes. In addition, bcl-2 MFI significantly correlated both with CD34 positivity (P = 0.001) and with CD34 MFI (P = 0.01), being CD34 antigen expressed in 65% of patients with a bcl-2 MFI >14, and only in 35% of AML cases with a bcl-2 MFI >14. When bcl-2 intensity expression was correlated with complete remission (CR) rate, a higher MFI was associated with a low CR rate after standard intensive chemotherapy. In particular, CR was achieved in 86% of patients with a bcl-2 MFI <14, but only in 57% of patients with a mfi >14 (P = 0.008). A further decrease of CR rate to 41% was observed in patients in whom a higher bcl-2 MFI was coupled with the presence of CD34 antigen on their blasts. By statistical analysis we also demonstrated that both bcl-2 high MFI (>14) and CD34 expression are independent prognostic factors for achieving CR in AML. These data raise the hypothesis that high values of bcl-2 may confer on myeloid blasts a higher resistance to standard chemotherapy. However, identification of patients with high expression of bcl-2 may be important for a different therapeutic approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lauria, F., Raspadori, D., Rondelli, D. et al. High bcl-2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells correlates with CD34 positivity and complete remission rate. Leukemia 11, 2075–2078 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400854
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400854
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Homoharringtonine is synergistically lethal with BCL-2 inhibitor APG-2575 in acute myeloid leukemia
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Spontaneous apoptosis and BCL2 gene expression as predictors of early death and short overall survival in acute leukemia patients: a prospective, case cohort study
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2021)
-
The application of BH3 mimetics in myeloid leukemias
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Inhibition of CDK9 by voruciclib synergistically enhances cell death induced by the Bcl-2 selective inhibitor venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
BCL2 overexpression: clinical implication and biological insights in acute myeloid leukemia
Diagnostic Pathology (2019)