Abstract
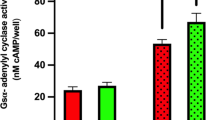
THE physiological actions of many hormones and neurotransmitters are mediated through activation of adenylate cyclase (ATP pyrophosphate lyase [cyclising] EC 4.6.1.1) by specific cell surface receptors for each substance. The consequent increases in intracellular cyclic AMP lead to activation of protein kinases and a host of alterations in cell physiology, depending on the type of cell stimulated1. Adrenergic receptors, responsive to β-hydroxylated catecholamines, were divided into α- and β-types by Ahlquist2 using classical pharmacological techniques. The β-adrenergic effects of catecholamines occur through a receptor-mediated stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity3. Although β-adrenergic receptors have often been described as ‘tightly coupled’ to adenylate cyclase, recent evidence suggests that the receptor and the enzyme are physically discrete entities4,5, probably the products of different genes6. We have found that HeLa cells contain β-adrenergic receptors and that the number of receptors per cell, but not the cellular content of adenylate cyclase, increases markedly during exposure of the cell to butyrate7. Here we present direct evidence that the HeLa cell β-adrenergic receptor can exist in a form either ‘coupled’ to or ‘uncoupled’ from adenylate cyclase. A model system for studies of receptor–adenylate cyclase interactions is described, and preliminary results of studies on the mechanism of coupling are reported.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robison, G. A., Butcher, R. W. & Sutherland, E. W. Cyclic AMP (Academic, New York, 1971).
Ahlquist, R. P. Am. J. Physiol. 153, 586–600 (1948).
Sutherland, E. W. & Robison, G. A. Pharmac. Rev. 18, 145–161 (1966).
Cuatrecasas, P. A. Rev. Biochem. 43, 169–214 (1974).
Orly, J. & Schramm, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 4410–4414 (1976).
Insel, P. A. et al. Molec. Pharmac. 12, 1062–1069 (1976).
Tallman, J. F., Smith, C. C. & Henneberry, R. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 873–877 (1977).
Henneberry, R. C. & Fishman, P. H. Expl Cell Res. 103, 55–62 (1976).
Steinberg, R. A., Levinson, B. B. & Tomkins, G. M. Cell 5, 29–35 (1975).
Van Obberghen, E., DeMeyts, P. & Roth, J. J. biol. Chem. 251, 6844–6851 (1976).
Rittenhouse, H. G. & Fox, C. F. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 57, 323–331 (1974).
Ash, J. G. & Singer, S. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 4575–4579 (1976).
Resch, K., Bouillon, D., Genisa, D. & Averdunk, R. Nature 265, 349–351 (1977).
Schwartz, J. P., Passoneau, J. V., Johnson, G. S. & Pastan, I. J. biol. Chem. 249, 4138–4143 (1974).
Ginsburg, E., Solomon, D., Sreevalsan, T. & Freese, E. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2457–2461 (1973).
Wright, J. A. Expl Cell Res. 78, 456–460 (1973).
Schneider, F. H. Biochem. Phamac. 25, 2309–2317 (1976).
Fishman, P. H., Simmons, J. L., Brady, R. O. & Freese, E. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 59, 292–299 (1974).
Henneberry, R. C., Fishman, P. H. & Freese, E. Cell 5, 1–9 (1975).
Simmons, J. L., Fishman, P. H., Freese, E. & Brady, R. O. J. Cell Biol. 66, 414–424 (1975).
Griffen, M. J., Price, G. H., Bazzell, K. L., Cox, R. P. & Ghosh, N. K. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 164, 619–623 (1974).
Ghosh, N. K. & Cox, R. P. Nature 259, 416–417 (1976).
Leder, A. & Leder, P. Cell 5, 319–322 (1975).
Altenburg, B. C., Via, D. P. & Steiner, S. H. Expl Cell Res. 102, 223–231 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HENNEBERRY, R., SMITH, C. & TALLMAN, J. Relationship between β-adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase in HeLa cells. Nature 268, 252–254 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/268252a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/268252a0