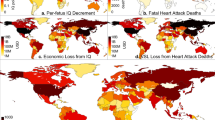
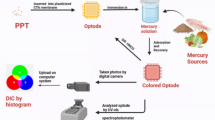
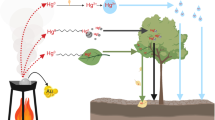
Abstract
RECENT studies have demonstrated the emission of mercury to the atmosphere from a variety of sources including contaminated industrial waste beds1–4. Investigations have also shown that vascular plants can take up both inorganic and organic mercury compounds through their root systems and transport them to the leaves5,6. Separate measurements of mercury emanations from the excised leaves of three vascular plant species have shown that there is a release of volatile mercury at room temperatures7. Thus, it would seem that vascular plants have the potential to take up mercury from a substrate, to transport it, and to emit it to the surrounding atmosphere through their leaves. However, no direct measurements of such emissions from living intact plants have been reported. We report here our examination of the common reed, Phragmites communis, growing along the shoreline of a mercury-contaminated lake and our finding that these plants, growing in their natural environment, actively release mercury to the atmosphere.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eshleman, A., Siegel, S. & Siegel, B. Nature 233, 471–472 (1971).
Siegel, B. & Siegel, S. Nature 241, 526 (1973).
Lindberg, S. & Turner, R. Nature 268, 133–136 (1977).
Johnson, D. L. & Braman, R. S. Envir. Sci. Technol. 8, 1003–1009 (1974).
Keeney, D., Dolar, S. & Chester, D. Envir. Lett. 1, 191–198 (1971).
Rahn, W. thesis, Georgia Inst. of Technol. (1973).
Siegel, S. M., Puerner, N. J. & Speitel, T. W. Physiol. Pl. 32, 174–176 (1974).
Braman, R. & Johnson, D. L. Envir. Sci. Technol. 8, 996–1003 (1974).
Kozuchowski, J. Analytica chim. Acta (in the press).
Krolikowska, J. Polskie Archwm Hydrobiol. 18, 347–358 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KOZUCHOWSKI, J., JOHNSON, D. Gaseous emissions of mercury from an aquatic vascular plant. Nature 274, 468–469 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274468a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274468a0
This article is cited by
-
Phytoextraction of high value elements and contaminants from mining and mineral wastes: opportunities and limitations
Plant and Soil (2020)
-
Opaque closed chambers underestimate methane fluxes of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2014)
-
Physiological Responses of Transgenic merA-TOBACCO (Nicotiana tabacum) to Foliar and Root Mercury Exposure
Water, Air, & Soil Pollution (2005)
-
Differential mercury volatilization by tobacco organs expressing a modified bacterial merA gene
Cell Research (2001)
-
Foliar exchange of mercury vapor: Evidence for a compensation point
Water, Air, & Soil Pollution (1995)