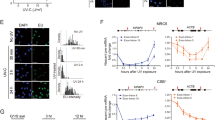
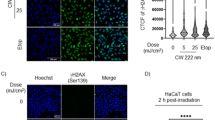
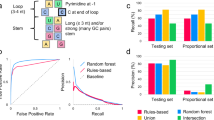
Abstract
RNA SPECIES C and D (nomenclature of Weinberg and Penman1) are among the most abundant of the long-lived2, homodisperse, low molecular weight nuclear RNAs3, and are present in all vertebrates tested4, but their function is unknown. They have several interesting characteristics: they seem to be transcribed from multiple-copy genes (102–103 genes per genome)5,6, to pass through the cytoplasm for a few minutes shortly after their transcription3,7–10, to have 5′-end caps that are very similar to those of eukaryotic mRNAs11,12, and to be present in heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein particles13,14. Here, we show that C and D RNA syntheses are unexpectedly sensitive to UV radiation in HeLa cells. The effect of UV radiation on RNA synthesis has been used to study the organisation of transcription units15. UV irradiation, causing random formation of pyrimidine dimers in DNA, results in premature termination of transcription. The probability of causing a UV lesion within a transcription unit is directly proportional to its length, making it possible to measure the distance between a gene and its promoter. The present UV sensitivity data are compatible with the transcription units for the low molecular weight (less than 200-nucleotide long1,11,12) RNA species C and D being as long as 5 kilobases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinberg, R. A. & Penman, S. J. molec. Biol. 38, 289–304 (1968).
Weinberg, R. & Penman, S. Biochim. biophys. Acta 190, 10–29 (1969).
Zieve, G. & Penman, S. Cell 8, 19–31 (1976).
Hellung-Larsen, P. & Frederiksen, S. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 58B, 273–281 (1977).
Engberg, J., Hellung-Larsen, P. & Frederiksen, S. Eur. J. Biochem. 41, 321–328 (1974).
Marzluff, W. F. et al. Biochemistry 14, 3715–3724 (1975).
Eliceiri, G. L. Cell 3, 11–14 (1974).
Frederiksen, S. & Hellung-Larsen, P. FEBS Lett. 58, 374–378 (1975).
Eliceiri, G. L. & Sayavedra, M. S. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 72, 507–512 (1976).
Eliceiri, G. L. & Gurney, T. Jr Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 81, 915–919 (1978).
Reddy, R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 249, 6486–6494 (1974).
Shibata, H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 3909–3920 (1975).
Deimel, B., Louis, C. & Sekeris, C. E. FEBS Lett. 73, 80–84 (1977).
Howard, E. F. Biochemistry 17, 3228–3236 (1978).
Sauerbier, W. Adv. Radiat. Biol. 6, 49–106 (1976).
Burdon, R. H., Martin, B. T. & Lal, B. M. J. molec. Biol. 28, 357–371 (1967).
Bernhardt, D. & Darnell, J. E. Jr J. molec. Biol. 42, 43–56 (1969).
Hackett, P. B. thesis, Univ. Colorado (1974).
Hackett, P. B. & Sauerbier, W. J. molec. Biol. 91, 234–256 (1975).
Goldberg, S., Schwartz, H. & Darnell, J. E. Jr Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 4520–4523 (1977).
Wellauer, P. K. & Dawid, I. Proc. natn. Acad. SCi. U.S.A. 70, 2827–2831 (1973).
Eliceiri, G. L. Biochim. biophys. Acta 425, 202–207 (1976).
Hackett, P. B., Traub, P. & Gallwitz, D. J. supramolec. Struct. Suppl. 2, 88 (1978).
Goldberg, S., Nevins, J. & Darnell, J. E. J. Virol. 25, 806–810 (1978).
Giorno, R. & Sauerbier, W. Cell 9, 775–783 (1976).
Giorno, R. & Sauerbier, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4374–4378 (1978).
Zieve, G., Benecke, B. J. & Penman, S. Biochemistry 16, 4520–4525 (1977).
Frederiksen, S., Hellung-Larsen, P. & Gram Jensen, E. FEBS Lett. 87, 227–231 (1978).
Eliceiri, G. L. J. Cell Biol. 53, 177–184 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ELICEIRI, G. Sensitivity of low molecular weight RNA synthesis to UV radiation. Nature 279, 80–81 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/279080a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/279080a0