Abstract
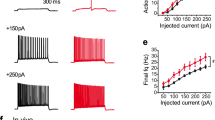
Hippocampal pyramidal cells, among the most-studied cortical neurones, display several interesting properties. In particular, intracellular recordings in both in vivo1 and in vitro2 preparations have shown that the pyramidal neurones of the CA3 region of the hippocampus have, in addition to the more conventional single spike, the capacity to generate spontaneous bursts of action potentials (APs). The burst-firing patterns have been well documented, but their underlying electrophysiological mechanisms are not completely understood. The bursts seem to be an intrinsic response of individual neurones and can be triggered by weak orthodromic stimulation or by direct depolarization of the somatic membrane. In molluscan and spinal systems, voltage-clamp techniques have revealed slow, voltage-sensitive, inward currents underlying this type of firing behaviour3–7. The use of these voltage-clamp techniques to study this phenomenon in hippocampal neurones has previously been precluded by the small size of the neurones and by the difficulty of recording from them in intact preparations. However, the development of methodology for voltage-clamping with a single microelectrode (SEC)8 and for the maintenance of hippocampal slices in vitro9 has made it possible for us to examine the membrane currents in these CA3 neurones. We report here a slow inward current in CA3 neurones and suggest that it is carried by calcium ions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kandel, E. R. & Spencer, W. A. J. Neurophysiol. 24, 243–259 (1961).
Wong, R. K. S. & Prince, D. A. Brain Res. 159, 385–390 (1978).
Wilson, W. A. & Wachtel, H. Science 186, 932–934 (1974).
Eckert, R. & Lux, H. D. J. Physiol., Lond. 254, 129–152 (1976).
Johnston, D. Brain Res. 107, 418–423 (1976).
Partridge, L. D., Thompson, S. H., Smith, S. J. & Connor, J. A. Brain Res. 164, 69–79 (1979).
Schwindt, P. C. & Crill, W. E. Brain Res. 120, 173–178 (1977).
Wilson, W. A. & Goldner, M. M. J. Neurobiol. 6, 411–422 (1975).
Schwartzkroin, P. A. Brain Res. 85, 423–436 (1975).
Schwartzkroin, P. A. Brain Res. 128, 53–68 (1977).
Johnston, D. Biophys. J. 25, 304a (1979).
Sperelakis, N., Schneider, M. F. & Harris, E. J. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 1565–1583 (1967).
Magura, I. S. J. Membrane Biol. 35, 239–256 (1977).
Hagiwara, S. in Membranes—A Series of Advances Vol. 3 (ed. Eisenman, G.) 359–381 (Dekker, New York, 1975).
Akaike, N., Lee, K. S. & Brown, A. M. J. gen. Physiol. 71, 509–531 (1978).
Tillotson, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 1497–1500 (1979).
Rall, W. Biophys. J. 9, 1483–1508 (1969).
Thompson, S. H. J. Physiol., Lond. 265, 465–488 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, D., Hablitz, J. & Wilson, W. Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones. Nature 286, 391–393 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/286391a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/286391a0
This article is cited by
-
Direct measurement of somatic voltage clamp errors in central neurons
Nature Neuroscience (2008)
-
Synaptic potentials and transfer functions of lamprey spinal neurons
Biological Cybernetics (1992)
-
Effects of cromakalim (BRL 34915) on potassium conductances in CA3 neurons of the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (1989)