Abstract
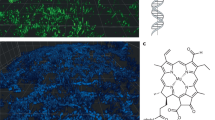
Electron-stimulated desorption (ESD) of ions and neutrals from surfaces has been used to study chemisorption in many simple gas–solid systems1,2, but there has been much less effort devoted to ESD studies with significant spatial resolution3–7. ESD contrasts with scanning electron microscopy because ESD signals depend sensitively on the coverage and binding of an adsorbed species1. Applying scanning ESD to biological surfaces permits the surface chemical variations to be mapped using simple low mass adsorbates8 in comparison with conventional electron microscopy of biological matters which relies on heavy-metal stain technology9. We show here how scanning ESD can complement scanning Auger electron microscopy in mapping the surface chemistry of biological substrates. A model biological substrate constructed from a deposited synthetic polypeptide monolayer (polymethyl-glutamate) is used as the controlled sample surface. Micrographs display a spatial variation in H+ desorption with a resolution of 10−4 cm. We also discuss limitations to resolution as dictated by signal-to-noise considerations. The contrast mechanism would be useful for studying the important biological surface problems such as membrane morphology, cell-interfacial composition, and cell-to-cell adhesion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madey, T. E. & Yates, J. T. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 8, 525–555 (1971).
Menzel, D. Surface Sci. 47, 370–383 (1975).
Rork, G. & Consoliver, R. F. Surface Sci. 10, 291–294 (1968).
Lichtman, D. & Campuzano, J. J. appl. Phys. Suppl. 2, 189–192 (1974).
Dylla, H. F. & King, J. G. Bull. Am. phys. Soc. 21, 241 (1976).
Joshi, A. & Davis, L. E. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 14, 1310–1313 (1977).
Poppa, H. & Bauer, E. Surface Sci. 97, L309–L312 (1980).
Weaver, J. C. & King, J. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2781–2784 (1973).
DeMee, P. B., Frederickson, R. G. & Pope, R. S. in Proc. 1977 Conf. on Scanning Electron Microscopy Vol. II, 83–92 (HT Research Institute, Chicago, 1977).
MacDonald, N. C., Hovland, C. T. & Gerlach, R. L. in Proc. 1977 Conf. on Scanning Electron Microscopy. Vol. I, 201–210 (IIT Research Institute, Chicago, 1977).
Gerlach, R. L. & Davis, L. E. J. Vac. Sci Technol. 14, 339–342 (1977).
Loeb, G. I. & Baier, R. E. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 27, 38–45 (1968).
Blodgett, K. B. J. Am. chem. Soc. 57, 1007–1022 (1935).
Mathewson, A. G. in Proc. int. Symp. on Plasma-Wall Interactions 517–536 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1977).
Powell, C. J. Surface Sci. 44, 29–46 (1974).
Davis, L. E., MacDonald, N. C., Palmberg, P. W., Riach, G. E. & Weber, R. E. Handbook of Auger Electron Spectroscopy (Perkin-Elmer, Eden Prairie, 1976).
Dawson, P. H. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. Ion Phys. 17, 447–467 (1975).
Hagstrum, H. D. Phys. Rev. 119, 940–952 (1960).
Weiss, R. Rev. Scient. Instrum. 32, 397–401 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dylla, H., Abrams, J., Hovland, C. et al. Scanning electron-stimulated desorption microscopy of model-biological surfaces. Nature 291, 401–404 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/291401a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/291401a0
This article is cited by
-
Uptake of trace metals by sediments and suspended particulates: a review
Hydrobiologia (1982)