Abstract
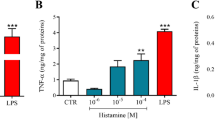
The release of histamine from human leukocytes is a useful in vitro model for studying allergic disease1. Many of the drugs used in the treatment of allergy and asthma (for example, isoprenaline and theophylline) are effective inhibitors of in vitro histamine release2. However, the anti-inflammatory steroids have not been found to inhibit the in vitro release of histamine from mast cells or basophils activated by immunological stimuli3–6. In view of the fact that the in vivo anti-allergic effects of steroids occur only 12‐24 h after administration7, we have re-examined the effects of these drugs on IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils after prolonged incubations. We report here a time-dependent inhibition of histamine release from human basophils by glucocortico-steroids. The relative activity of a series of steroids as inhibitors of histamine release correlates well with the relative in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of the same compounds. These results suggest that the basophil may be an in vivo target of the anti-inflammatory steroids and that inhibition of this cell type may account for some of the activity of steroids in preventing inflammation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lichtenstein, L. M., Marone, G., Thomas, L. L. & Malveaux, F. J. invest. Derm. 71, 65–69 (1978).
Bourne, H. R. et al. Science 184, 19–28 (1974).
Norn, S. Acta pharmac. tox. 22, 369–378 (1965).
Schmutzler, W. & Freundt, G. P. Int. Archs Allergy appl. Immun. 49, 209–212 (1975).
Thomas, R. O. & Whittle, B. J. R. Br. J. Pharmac. 57, 474P–475P (1976).
Lewis, G. P. & Whittle, B. J. R. Br. J. Pharmac. 61, 229–235 (1977).
Liddle, G. W. Clin. Pharmac. Ther. 2, 615–635 (1961).
Lichtenstein, L. M. & Osler, A. G. J. exp. Med. 120, 507–530 (1964).
Gilman, A. G., Goodman, L. S. & Gilman, A. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics 6th edn (Macmillan, New York, 1980).
Ballard, P. L., Carter, J. P., Graham, B. S. & Baxter, J. D. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 41, 290–304 (1975).
Dausse, J. P. et al. Molec. Pharmac. 13, 948–955 (1977).
Meikle, A. W., Weed, J. A. & Tyler, F. H. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 41, 717–721 (1975).
Peterson, R. E., Pierce, C. E., Wyngaarden, J. B., Bunim, J. J. & Brodie, B. B. J. clin. Invest. 37, 1301–1312 (1957).
Blackwell, G. J., Flower, R. J., Nijkamp, F. P. & Vane, J. R. Br. J. Pharmac. 62, 79–89 (1978).
Tam, S., Hong, S. L. & Levine, L. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 203, 162–168 (1977).
Cantrill, H. L., Waltman, S. R., Palmberg, P. F., Zink, H. A. & Decker, B. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 40, 1073–1077 (1975).
Vassalli, J. D., Hamilton, J. & Reich, E. Cell 8, 271–281 (1976).
Dvorak, A. M., Mihm, M. C. & Dvorak, H. F. J. Immun. 116, 687–695 (1976).
Askenase, P. W., Haynes, D. & Hayden, B. J. J. Immun. 117, 216–224 (1976).
MacGlashan, D. W. & Lichtenstein, L. M. J. Immun. 124, 2519–2521 (1980).
Siraganian, R. P. Analyt. Biochem. 57, 383–388 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schleimer, R., Liechtenstein, L. & Gillespie, E. Inhibition of basophil histamine release by anti-inflammatory steroids. Nature 292, 454–455 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/292454a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/292454a0
This article is cited by
-
Basophil responsiveness in chronic urticaria
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2009)
-
Immunopharmacology of human mast cells and basophils
International Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Research (1998)
-
An overview of glucocorticoid anti-inflammatory actions
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (1993)
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids and cyclosporin A on human basophils
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (1993)