Abstract
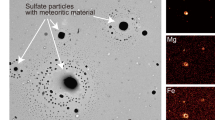
Although sulphur is the most common element in the Antarctic aerosol, no more than 6% of the sulphate can be of direct marine origin1. Cadle et al.2 and Bigg3 found much of the aerosol in the Antarctic to be a complex, partially neutralized, acid sulphate, although essentially ‘pure’ H2SO4 and (NH4)2SO4 particles were common. Efforts to analyse size-segregated aerosol samples chemically have been generally unsuccessful. There is, therefore, a question of the origin of the sulphate component of the Antarctic aerosol. I consider here the contributions that Antarctic volcanic activity may make to the sulphate content of the Antarctic aerosol.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maenhaut, W., Zoller, W. H., Duce, R. E. & Hoffman, G. L. J. geophys. Res. 84, 2421–2431 (1979).
Cadle, R. D., Fischer, W. H., Frank, E. R. & Lodge, J. P. J. J. atmos. Sci 25, 100–103 (1968).
Bigg, E. K. J. appl. Met. 19, 521–533 (1980).
Shaw, G. E. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 17, 1983–1998 (1979).
Delmas, R. & Boutron, C. Atmos. Envir. 12, 723–728 (1978).
Shaw, G. E. Atmos. Envir. 14, 911–921 (1980).
Bonsang, B., Nguyen, B. C., Gaudry, A. & Lambert, G. J. geophys. Res. 85, 7410–7416 (1980).
Herron, M. M. J. geophys. Res. 87, 3052–3060 (1982).
Rahn, K. A. & McCaffrey, R. J. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 338, 486–503 (1980).
Boutron, C. & Delmas, R. Ambio 9, 210–215 (1980).
Ng, A. & Patterson, C. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 45, 2109–2121.
Polian, G., & Lambert, G. J. Volcan. Geotherm. 6, 125–137 (1979).
Gonzalez-Ferran, O. EOS 63, 538 (1982).
Quartermain, L. B. South to the Pole—The Early History of the Ross Sea Sector, Antarctica (London, 1967).
Kyle, P. R., Guggenbach, W. F. & Keys, H. J. R. Antarctic J. 2, 270–271 (1976).
Bodhaine, B. A. & Murphy, M. E. J. Aerosol Sci. 11, 305–312 (1980).
Waggoner, A. P., Ahlquist, N. C. & Charlson, R. J. Atmospheric Aerosols: their Optical Properties (NASA CP-2004, 1976).
Radke, L. F., Hobbs, P. V. & Stith, J. L. Geophys. Res. Lett. 3, 93–96 (1976).
Stith, J. L., Hobbs, P. V. & Radke, L. F. J. geophys. Res. 83, 4009–4017 (1978).
Minnaert, M. The Nature of Light and Color (Dover, New York, 1954).
Radke, L. F. Antarctic J. 16, 196–197 (1981).
Radke, L. F., Hobbs, P. V. & Eltgroth, M. W. J. appl. Met. 19, 715–722 (1980).
Pruppacher, H. R. & Klett, J. D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, 714 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1978).
Zettwoog, P. & Haulet, E. Atmos. Envir. 12, 795–796 (1978).
Shaw, G. J. geophys. Res. 87, 4309–4313 (1982).
Taljaard, J. J. Met. Monogr. 13, 139–211 (1967).
Hogan, A. W. J. appl. Met. 14, 550–559 (1975).
Hogan, A. w. J. appl. Met. 18, 741–749 (1979).
Hobbs, P. V., Tuell, J. P., Radke, L. F., Hegg, D. A. & Eltgroth, M. W. J. geophys. Res. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radke, L. Sulphur and sulphate from Mt Erebus. Nature 299, 710–712 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299710a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299710a0
This article is cited by
-
Rates of sulfur dioxide and particle emissions from White Island volcano, New Zealand, and an estimate of the total flux of major gaseous species
Bulletin of Volcanology (1986)
-
Fluxes, sizes, morphology and compositions of particles in the Mt. Erebus volcanic plume, December 1983
Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry (1986)
-
Rate of sulphur dioxide emission from Erebus volcano, Antarctica, December 1983
Nature (1985)