Abstract
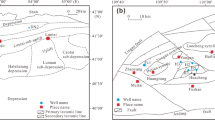
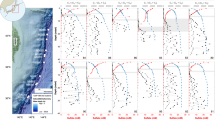
Annual discharges of organic matter into Tokyo Bay have been estimated to be ∼1.5–6.6×105 tonnes (expressed as carbon) during 1973–761. We report here new findings of alkylbenzene pollution of sediments from the bay and adjacent areas. The pollution level of alkylbenzenes (0.5–1.4 µg per g dry sediment) is comparable with that of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The vertical distribution of alkylbenzenes in a Tokyo Bay sediment indicates that the pollution started around 1960—at the same time as alkylbenzenesulphonates (synthetic detergents) began to be used widely in the Tokyo area. The alkylbenzenes in the sediments are considered to have been carried with alkylbenzenesulphonates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogura, N. Bull, Coastal Oceanogr. 16, 92–100 (1979).
Stenhagen, E., Abrahamsson, S. & McLafferty, F. W. (eds) Registry of Mass Spectral Data Vols 2, 3 Wiley, New York (1974).
Hon-nami, H. & Hanya, T. Jap. J. Limnol. 41, 1–4 (1980).
Matsumoto, E. J. geol. Soc. Jap. 81, 301–306 (1975).
Ambe, Y. Nature 239, 24–25 (1972).
Gledhill, W. E. Adv. appl. Microbiol. 17, 265–293 (1974).
Encyclopedia Genre Japonica Vol. 15, 390 Shogakukan, Tokyo, (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiwatari, R., Takada, H., Yun, SJ. et al. Alkylbenzene pollution of Tokyo Bay sediments. Nature 301, 599–600 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/301599a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/301599a0
This article is cited by
-
Monitoring of linear alkyl benzenes (LABs) in riverine and estuarine sediments in Malaysia
Environmental Geochemistry and Health (2022)
-
Nickel-catalysed anti-Markovnikov hydroarylation of unactivated alkenes with unactivated arenes facilitated by non-covalent interactions
Nature Chemistry (2020)
-
Monitoring of sewage pollution in the surface sediments of coastal ecosystems using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) as molecular markers
Journal of Soils and Sediments (2020)
-
Evaluation of distribution and sources of sewage molecular marker (LABs) in selected rivers and estuaries of Peninsular Malaysia
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2016)
-
Indicators of terrestrial biogenic hydrocarbon contamination and linear alkyl benzenes as land-base pollution tracers in marine sediments
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2015)