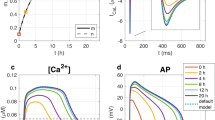
Abstract
Douglas and Rubin1 suggested that “the role of acetylcholine as a transmitter at the adrenal medulla is to cause some brief change in medullary cells which allows Ca ions to penetrate them and trigger the catecholamine ejection process”. The Ca2+-channel blocking agents, verapamil, nifedipine and nitrendipine, have been used widely to investigate the properties of slow Ca2+ channels in a variety of tissues2, including the adrenomedullary chromaffin cell3,4. Recently, small modifications to the nifedipine molecule produced a derivative, BAY-K-8644(methyl-l,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylate), that in contrast to the Ca2+-channel blocking agents, stimulated cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contractility5. We have tested whether this compound behaves as a Ca2+-channel activator at the chromaffin cell membrane as shown by Schramm et al.5 in smooth muscle cells. The experiments described here strongly suggest that it does so.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Douglas, W. W. & Rubin, R. P. J. Physiol., Lond. 159, 40–57 (1961).
Fleckenstein, A. A. Rev. Pharmac. Tox. 17, 149–166 (1977).
Ceña, V., Nicolas, G. P., Sánchez-García, P., Kirpekar, S. M. & García, A. G. Neuroscience (in the press).
Pinto, J. E. B. & Trifaró, J. M. Br. J. Pharmac. 57, 127–132 (1976).
Schramm, M., Thomas, G., Towart, R. & Franckowiak, G. Nature 303, 535–537 (1983).
García, A. G., Hernández, M., Horga, J. F. & Sánchez-García, P. Br. J. Pharmac. 68, 571–583 (1980).
Douglas, W. W., Kanno, T. & Sampson, S. R. J. Physiol, Lond. 191, 107–121 (1967).
Ishikawa, K. & Kanno, T. Jap. J. Physiol. 28, 275–289 (1978).
Bellemann, P., Ferry, D., Lübbecke, F. & Glossmann, H. Arzneim. Forsch. 31, 2064–2067 (1981).
Frías, J., Alonso, F. G., Ceña, V., Sánchez-García, P. & García, A. G. in Molecular Neurobiology of Peripheral Catecholaminergic Systems (ed. García, A. G.) 151 (Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, 1982).
Baker, P. F. & Rink, T. J. J. Physiol., Lond. 253, 593–620 (1975).
Kirpekar, S. M. & Prat, J. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 2081–2083 (1979).
Kirpekar, S. M., García, A. G. & Schiavone, M. T. Adv. Biosci. 36, 55–62 (1982).
Douglas, W. W. & Poisner, A. M. J. Physiol., Lond. 162, 385–392 (1962).
Kilpatrick, D. L., Slepetis, R. L., Corcoran, J. J. & Kirshner, N. J. Neurochem. 38, 427–435 (1982).
Holz, R. W., Senter, R. A. & Frye, R. A. J. Neurochem. 39, 635–646 (1982).
Fenwick, E. M., Marty, A. & Neher, E. J. Physiol., Lond. 331, 599–635 (1982).
Shellenberger, M. K. & Gordon, J. H. Analyt. Biochem. 39, 356–372 (1971).
Aunis, D. & García, A. G. Br. J. Pharmac. 72, 31–40 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García, A., Sala, F., Reig, J. et al. Dihydropyridine BAY-K-8644 activates chromaffin cell calcium channels. Nature 309, 69–71 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/309069a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/309069a0
This article is cited by
-
Old and emerging concepts on adrenal chromaffin cell stimulus-secretion coupling
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2018)
-
Hydrogen sulphide facilitates exocytosis by regulating the handling of intracellular calcium by chromaffin cells
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2018)
-
Simvastatin reduces adrenal catecholamine secretion evoked by stimulation of cholinergic nicotinic and angiotensinergic AT1 receptors
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2018)
-
L-type calcium channels in exocytosis and endocytosis of chromaffin cells
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2018)
-
Inhibition of N and PQ calcium channels by calcium entry through L channels in chromaffin cells
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2009)